What is Cost reduction? and cost control
Cost control
Concept of cost control
Modern management is becoming increasingly cost-conscious and is constantly in search of new ways of controlling costs and eliminating wastes. One of the basis objectives of cost accounting is to achieve cost control. The effectiveness of cost account ting is jested primarily from the ex tern to whom it has been able to bring about a control over the manufacturing and other expenses.
The terminology of cost accountancy of the institute of cost and management accountants London, defines cost control' as " the guidance and regulation by executive action of the costs of operating an under taking, particular where such action is guided by cost accounting."
In cost control, the first step is to set up the target to be achieved, i.e., the goal or objective to be attained. The cost control system guides the organization to reach threat goal. For this purpose, budgets or standards are uses. These budgets or standard provides the yardstick against which actual cost and performances may be compared. If at any stage, it is noticed that the expenses are showing a trend away from the goal, resulting thereby in a variation from the target, the cost control systems help to regulate this trend and to eliminate the variations. This guidance and regulation is by executive action, i.e., through an action taken by the executive who is responsible for the incurring of the expenditure. It should be clearly understood that a cost accountants by him does not control the expenses. He merely assists in the control of expense since expenditures can be controlled only by the person who insures the expenditure. The cost accountant brings to the notice of the executive concerned, the exact point on which an action is required of him for regulating the expenses. Thus, cost control is the guidance and regulation through an executive actions and this executive is exercised in respect of all the expenses incurred in operating an undertaking. Cost control comparisons all procedures and measures by which the cost of carrying out an activity is kept under check and aims at ensuring that costs do not go beyond a certain level.
Process/ steps in cost control
Efficient organization and operation of cost control systems involves the following steps:
• Setting up the targets.
• Measurement of the actual performance and actual cost.
• Comparison of actual with the target to ascertain variances.
• Analysis of variances (between the target and the actual) to their cause.
• Taking such corrective actions as are necessary to eliminate the variations.
Tools and technique of cost control
Cost control can be exercised by adopting the following tools and techniques:
• Material control
• Labor control
• Overhead control
• Budgetary control
• Standard costing
• Capital expenditure control
• Productivity ratio
Cost reduction
Meaning of cost reduction
Generally, cost reduction means to minimize and control the expenses incurred. In other words, the aim of cost reduction is to see whether there is any possibility in bringing about a saving in the cost incurred in materials, labour, overheads etc.
Institute of cost and management accountants, London defines "cost reduction is to be as the achievement of real permanent reduction in the unit cost of goods manufactured or services rendered without impairing their suitability for the use intended or diminution in the quality of the product."
Thus, cost reduction means an achievement of real and permanent reduction in the unit cost of goods produced or services rendered without impairing their quality or function suitability.
The above definition brings out the following as the essential features of cost reduction:
a. Reduction should be real: the reduction must be a real one in the course of manufacture of goods or services rendered through increase in productivity.
b. Reduction should be permanent: the reduction must be permanent one. Reduction in cost due to windfalls, reduction in taxes due to change in government policy or any other fortuitous receipts do not fall within the preview of cost reduction.
c. Quality or utility to be maintained: the reduction should not be at the cost of essential characteristic and quality or utility of the products or services rendered.
Advantages of cost reduction
The main advantages of cost reduction may be summarized as follows:
a. Cost reduction increase the profit of an undertaking which ultimately provides a basis for more dividends to shareholders, higher rate of bonus to staff and retention of more profit for the business.
b. Due to the increase in profit, management may spend more in providing amenities to worker. It will ensure more cordial relationship between management and workers and the labor turnover.
c. Increase profitability of the undertaking due to cost reduction adds it its goodwill.
d. Reaction in the unit cost indicates better productivity and efficiency. The efficiency of a firm may benefit the member of the industry as a whole.
e. Higher profitability will ensure increased process to the government by way of station.
f. Cost reduction may lead to lower export prices resulting in higher total experts.
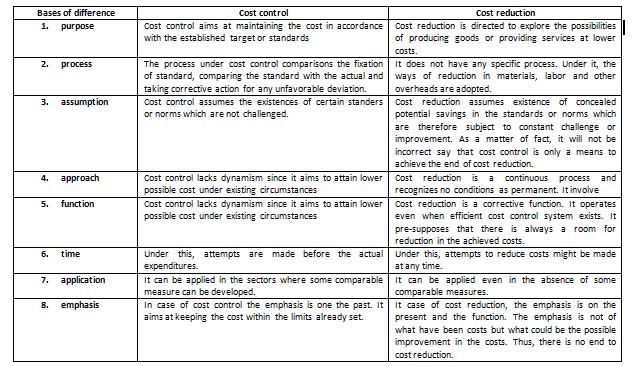
Difference between cost control an cost reduction
Cost control is the technique of minimizing the cost. The main purpose of controlling the cost is to decrease per unit cost of production. The difference the two can be introduced as follows:
Difference between cost control an cost reduction
Cost control is the technique of minimizing the cost. The main purpose of controlling the cost is to decrease per unit cost of production. The difference the two can be introduced as follows:
Areas or scopes of cost reduction
The scope of cost reduction is very wide and it is not practicable to develop the areas in which cost reduction may be applied fully. Any areas wherein costs are incurred has the scope for cost reduction and it should be thought that there is no scope for cost reduction in any particular area. However, the following areas have the largest scope of cost reduction:
a. product design
The design of the product provides the maximum scope for cost reduction. Since product design is the first step in production, cost reduction at this stage is likely to benefit throughout the manufacturing life of the product. Possible in the reduction of cost should be investigated, both, while improving existing design or introducing new design or introducing new designs. Some of the important factors in product improvement are:
• quality of the product
• Unnecessary weight, materials content, machine or labor operations.
• Waste and losses to be eliminated.
• Proper designing of the product.
b. Factory organization and production methods
Cost reduction Is affected to a great extent by improving factory organization and production methods in the form of clear-cut lines of authority and responsibility, well defined channels of communications, coordination and co-operation and co-operation between various executives, new manufacturing techniques, new process, new production methods, etc.
c. Production planning and control
Production planning also affects the cost reduction. The location and lay-out of the factory have significant influence on cost. Of Corse, the factory location cannot behaves so easily but its layout can be organized on core scientific lines as to as reduce the cost of production.
The chartered institute of management accounts, London, in its publication on cost reduction, has laid down the following principles for developing a sound production planning systems:
i. Production planning should be based on realistic and detailed sales forecast.
ii. Efficient production systems requires fullest possible employment of suitable production facilities, elimination of unnecessary movement and handling of materials provision of adequate working instructions, drawings tools, etc. and the most economical storage of stocks.
The design of a production systems is dependent on its location because the resulting physical factors in fluent layout and also because of the fact that the location determines operating and capital costs, in so for as physical factors of plant design are concerned, location may determine the following costs:
1. Whether or not power is to be purchased.
2. The extent of air conditioning or humidification required.
3. Whether local sub-contracting facilities for component are available or whether provision for the manufacturing of components has to be made in the factory.
4. Storage space requirements depending on the availability of raw materials in the vicinity.
5. The types of transportation facilities available for receiving raw materials and dispatching finished goods, etc.
From the standpoint of costs, transportation cost, labor costs, costs of land s construction cost, etc. will be influenced by the location of the factory.
d. Administration areas
There is simple scope of cost reduction in this area because cost reduction is a top management problem. Office should be reorganized if there is scope for improvement in the efficiency of persons engaged in the office. Use of unnecessary from should be avoided to save the cost of stationary and labor cost involved for compiling them. Effort should be made to reduce the expenses of telephone, lighting and travelling g but not at the cost of efficiency.
e. Marketing areas
The various activities which can be bought under the cost reduction programmers include market search, advertisement packing, warehouse, distributions, after-sales services etc. sales performance can be improved by market ABC analysis of customers. Customers can be classified in three categories A,B and C. a category customers means customers having about 10% if total dispatches but cover about 70% of sales value, B category customers means customers having about 20% of total dispatches but covering about 25% of sales value and C category customers means customers having about 70% of total dispatches but covering about 5% of total sales value. In this way of categorization of customers, sales efforts will be better focuses and there will be reduction in market cost.
f. Finance areas
With the increasing difficult in procuring finance, management should eliminate useless investment. To be able to do so, it must critically examine the amount of working capital and fixed capital needed and the financial convenience of reducing them. Wasteful use of capital use capital is as bad as inadequate capital. Over and under capitalization are both danger signals: what is needed is fair capitalization. Capital should be procured at economical cost and it should be economically used so as to give the maximum return. Fixed assets and inventories which cannot be economically used should be sold; the money realized. Fixed assets and inventories which cannot be economically used should be sold; the money realized from their sale should be reinvested in more profitable channels.
g. Purchase and material control
1. Direct material cost reduction: direct material generally constitutes 50% of the cost of a product.
The following steps may be helpful in reducing material costs:
• Control should be exercised on purchasing of raw materials. They should be purchase in economical lost at economic prices from reliable dealers at appropriate times. The adoption of the japans just in time (JIT) techniques may greatly reduce the material costs.
• The various inventory control techniques, VIZ, fixation and observance of inventory levels (maximum, minimum and re-order levels) of inventory, ABC analysis, ageing schedule, perpetual inventory systems followed by continuous stock taking etc. should be adopted.
• All efforts should be made to avoid/ minimize losses and wastage of raw materials. Economic should also be maintaining in handling cost of raw materials.
2. Direct labor cost reduction: direct labor constitutes second important element of the cost of a product. Cost reduction in labor is possible through proper organization and functioning of the personnel, works study and engineering department's .the personnel department is concerned with finding out the right mind for the right job and the right man. The engineering and works study department is concerned with job studies, time studies and motion studies. All these functions go a long way in reducing costs and therefore all efforts should be made to discharge them with the intention to increase the productivity and reduce costs.
3. Overhead cost reduction: the term overhead includes factory overheads. Office overhead and selling and distribution overheads. Considerable saving can be achieved in the overhead costs through cooperation of the concerned executives at different levels and creating a sense of conscious amongst them as examined below. The reduction in administrative costs whether in factory, office or selling and distribution divisions can be achieved through the following measures:
• Staff can be reduced by having evaluation of jobs.
• Utilization of machinery and equipment can be improved through systematic supervision.
• Productivity of workers and executives can be increased through smooth flow of work.
• Expenditure on printing, passage ad telephone can be reduced by exercising appropriate control measures.
Similarly, selling and distributions costs can be reduced by examining the following suspects:
• Whether the channels of distribution are efficient and economical.
• Whether distributional and selling methods ensure promptness.
• Whether there is an effective system of sales promptness.
• Whether the market research is adequate.
• Whether market method both for home and export trade are satisfactory.
• Whether there are many possibilities of reducing the selling and distribution costs without impairing the efficiency of the sales division.
Tools and techniques of cost reduction
The various tools and techniques used for achieving cost reduction are practically the same which have been suggested for cost control. Some of these are:
The scope of cost reduction is very wide and it is not practicable to develop the areas in which cost reduction may be applied fully. Any areas wherein costs are incurred has the scope for cost reduction and it should be thought that there is no scope for cost reduction in any particular area. However, the following areas have the largest scope of cost reduction:
a. product design
The design of the product provides the maximum scope for cost reduction. Since product design is the first step in production, cost reduction at this stage is likely to benefit throughout the manufacturing life of the product. Possible in the reduction of cost should be investigated, both, while improving existing design or introducing new design or introducing new designs. Some of the important factors in product improvement are:
• quality of the product
• Unnecessary weight, materials content, machine or labor operations.
• Waste and losses to be eliminated.
• Proper designing of the product.
b. Factory organization and production methods
Cost reduction Is affected to a great extent by improving factory organization and production methods in the form of clear-cut lines of authority and responsibility, well defined channels of communications, coordination and co-operation and co-operation between various executives, new manufacturing techniques, new process, new production methods, etc.
c. Production planning and control
Production planning also affects the cost reduction. The location and lay-out of the factory have significant influence on cost. Of Corse, the factory location cannot behaves so easily but its layout can be organized on core scientific lines as to as reduce the cost of production.
The chartered institute of management accounts, London, in its publication on cost reduction, has laid down the following principles for developing a sound production planning systems:
i. Production planning should be based on realistic and detailed sales forecast.
ii. Efficient production systems requires fullest possible employment of suitable production facilities, elimination of unnecessary movement and handling of materials provision of adequate working instructions, drawings tools, etc. and the most economical storage of stocks.
The design of a production systems is dependent on its location because the resulting physical factors in fluent layout and also because of the fact that the location determines operating and capital costs, in so for as physical factors of plant design are concerned, location may determine the following costs:
1. Whether or not power is to be purchased.
2. The extent of air conditioning or humidification required.
3. Whether local sub-contracting facilities for component are available or whether provision for the manufacturing of components has to be made in the factory.
4. Storage space requirements depending on the availability of raw materials in the vicinity.
5. The types of transportation facilities available for receiving raw materials and dispatching finished goods, etc.
From the standpoint of costs, transportation cost, labor costs, costs of land s construction cost, etc. will be influenced by the location of the factory.
d. Administration areas
There is simple scope of cost reduction in this area because cost reduction is a top management problem. Office should be reorganized if there is scope for improvement in the efficiency of persons engaged in the office. Use of unnecessary from should be avoided to save the cost of stationary and labor cost involved for compiling them. Effort should be made to reduce the expenses of telephone, lighting and travelling g but not at the cost of efficiency.
e. Marketing areas
The various activities which can be bought under the cost reduction programmers include market search, advertisement packing, warehouse, distributions, after-sales services etc. sales performance can be improved by market ABC analysis of customers. Customers can be classified in three categories A,B and C. a category customers means customers having about 10% if total dispatches but cover about 70% of sales value, B category customers means customers having about 20% of total dispatches but covering about 25% of sales value and C category customers means customers having about 70% of total dispatches but covering about 5% of total sales value. In this way of categorization of customers, sales efforts will be better focuses and there will be reduction in market cost.
f. Finance areas
With the increasing difficult in procuring finance, management should eliminate useless investment. To be able to do so, it must critically examine the amount of working capital and fixed capital needed and the financial convenience of reducing them. Wasteful use of capital use capital is as bad as inadequate capital. Over and under capitalization are both danger signals: what is needed is fair capitalization. Capital should be procured at economical cost and it should be economically used so as to give the maximum return. Fixed assets and inventories which cannot be economically used should be sold; the money realized. Fixed assets and inventories which cannot be economically used should be sold; the money realized from their sale should be reinvested in more profitable channels.
g. Purchase and material control
1. Direct material cost reduction: direct material generally constitutes 50% of the cost of a product.
The following steps may be helpful in reducing material costs:
• Control should be exercised on purchasing of raw materials. They should be purchase in economical lost at economic prices from reliable dealers at appropriate times. The adoption of the japans just in time (JIT) techniques may greatly reduce the material costs.
• The various inventory control techniques, VIZ, fixation and observance of inventory levels (maximum, minimum and re-order levels) of inventory, ABC analysis, ageing schedule, perpetual inventory systems followed by continuous stock taking etc. should be adopted.
• All efforts should be made to avoid/ minimize losses and wastage of raw materials. Economic should also be maintaining in handling cost of raw materials.
2. Direct labor cost reduction: direct labor constitutes second important element of the cost of a product. Cost reduction in labor is possible through proper organization and functioning of the personnel, works study and engineering department's .the personnel department is concerned with finding out the right mind for the right job and the right man. The engineering and works study department is concerned with job studies, time studies and motion studies. All these functions go a long way in reducing costs and therefore all efforts should be made to discharge them with the intention to increase the productivity and reduce costs.
3. Overhead cost reduction: the term overhead includes factory overheads. Office overhead and selling and distribution overheads. Considerable saving can be achieved in the overhead costs through cooperation of the concerned executives at different levels and creating a sense of conscious amongst them as examined below. The reduction in administrative costs whether in factory, office or selling and distribution divisions can be achieved through the following measures:
• Staff can be reduced by having evaluation of jobs.
• Utilization of machinery and equipment can be improved through systematic supervision.
• Productivity of workers and executives can be increased through smooth flow of work.
• Expenditure on printing, passage ad telephone can be reduced by exercising appropriate control measures.
Similarly, selling and distributions costs can be reduced by examining the following suspects:
• Whether the channels of distribution are efficient and economical.
• Whether distributional and selling methods ensure promptness.
• Whether there is an effective system of sales promptness.
• Whether the market research is adequate.
• Whether market method both for home and export trade are satisfactory.
• Whether there are many possibilities of reducing the selling and distribution costs without impairing the efficiency of the sales division.
Tools and techniques of cost reduction
The various tools and techniques used for achieving cost reduction are practically the same which have been suggested for cost control. Some of these are:
• Value analysis or value engineering Work study
• Job evaluation or value merit rating Production planning and control
• Organization and method study Operations and method study
• Rationalization Quality control
• Economic order quality Use of better technology
• Mechanization and automation Standardization
• Simplification classification and codification
• variety reduction improvement in the design of a product
• market research inventory management and control
Essentials for success of cost reduction programmers
Cost reduction programmers aims at improvements of human efforts at all levels of the organization, which help in reducing costs. It may be a short-term or long-term program. A short-term programmer is undertaken for sorting out immediate problem; e.g., a problem involving controlling wastages and inefficiencies is certain departments, which are likely to push up the cost and may also require capital expenditure. It involves setting up of the target return on capital employed and developing a scheme for its achievement through various cost reduction measures:
The following are the essential requisites for successful implementation of a cost reduction programmer:
a. There should be a separate cost reduction cell responsible for proper planning and implementation of the cost reduction programme.
b. There should be an efficient system of management reporting at all levels of management.
c. The programme should have support from the top management. It is a continuous process and, therefore, should not be allowed to degenerate into a routine affair.
d. There should be an operation and research procedure.
e. There should be close co-operation amongst different executives concerned with the programme. Each departmental head should be given a list of the areas where he is expected to affect economies in cost. Moreover, he should also be encouraged to put forward his own suggestions for improvement.
f. There should be regular followed-up to the plan and continuous appraisal of the programme performed with the actual cost reduction performance.
g. The plan should not be confined only to reducing costs but should also examine whether expenditure is really required or not. In other words, there should be efforts to eliminate uneconomic and unnecessary activities.
The following are the essential requisites for successful implementation of a cost reduction programmer:
a. There should be a separate cost reduction cell responsible for proper planning and implementation of the cost reduction programme.
b. There should be an efficient system of management reporting at all levels of management.
c. The programme should have support from the top management. It is a continuous process and, therefore, should not be allowed to degenerate into a routine affair.
d. There should be an operation and research procedure.
e. There should be close co-operation amongst different executives concerned with the programme. Each departmental head should be given a list of the areas where he is expected to affect economies in cost. Moreover, he should also be encouraged to put forward his own suggestions for improvement.
f. There should be regular followed-up to the plan and continuous appraisal of the programme performed with the actual cost reduction performance.
g. The plan should not be confined only to reducing costs but should also examine whether expenditure is really required or not. In other words, there should be efforts to eliminate uneconomic and unnecessary activities.
1. Write the meaning of cost control.
Cost control is a system of cost accounting that aims at maintaining the cost in accordance with the established targets or standards. It comparisons the fixation of standard, comparing the star with the actual and taking corrective actions for any unfavorable deviation. It assumes the existence of certain standards or norms which are not challenged. Cost control lacks dynamism since it aims to attain lower possible costs under existing circumstances it is a preventive function. Under it, costs are optioned before they are incurred.
2. Write the meaning of cost reduction.
Cost reduction is directed to explore the producing goods or providing services at lower costs. It does not have any specific process. Under it, the ways of reduction in materials, labor and other overheads are adopted. It is a corrective function and a continues process and recognizes no conditions as permanent. It assumes existence of concealed potential savings in the standards or norms which are therefore subject to constant challenge or improvement.
3. Write any five differences between cost control and cost reduction.
Cost control is the techniques of minimizing the cost. The main purpose of controlling the cost is to decrease per unit cost of production. The difference between the two can be introduced as follows:
a. Purpose: cost control aims at maintaining the cost in accordance with the established target or standard but cost reduction is directed to explore the possibilities of producing goods or providing services at lower costs.
b. Process: cost control comprises the fixation of standard, comparing the standard with the actual and taking corrective action for any unfavorable deviation but cost reduction does not have any specific process. Under it, the ways of reduction in have any specific process. Under it, the ways of reduction in materials, labor and other overheads are adopted.
c. Assumption: cost control assumes the existence of certain standard or norms which are not challenged whereas cost reduction assumes existence of concealed potential savings in the standard or moms which are the fore subject to constant challenge or improvement.
d. Approach: cost control lacks dynamism since it aims to attain lower possible cost under existing circumstances but cost reduction is a continuous process and recognizes no conditions as permanent.
e. Function: cost control is a preventive function. Under it, costs are optimized before they are uncured but cost reduction is a corrective function.
Cost control is a system of cost accounting that aims at maintaining the cost in accordance with the established targets or standards. It comparisons the fixation of standard, comparing the star with the actual and taking corrective actions for any unfavorable deviation. It assumes the existence of certain standards or norms which are not challenged. Cost control lacks dynamism since it aims to attain lower possible costs under existing circumstances it is a preventive function. Under it, costs are optioned before they are incurred.
2. Write the meaning of cost reduction.
Cost reduction is directed to explore the producing goods or providing services at lower costs. It does not have any specific process. Under it, the ways of reduction in materials, labor and other overheads are adopted. It is a corrective function and a continues process and recognizes no conditions as permanent. It assumes existence of concealed potential savings in the standards or norms which are therefore subject to constant challenge or improvement.
3. Write any five differences between cost control and cost reduction.
Cost control is the techniques of minimizing the cost. The main purpose of controlling the cost is to decrease per unit cost of production. The difference between the two can be introduced as follows:
a. Purpose: cost control aims at maintaining the cost in accordance with the established target or standard but cost reduction is directed to explore the possibilities of producing goods or providing services at lower costs.
b. Process: cost control comprises the fixation of standard, comparing the standard with the actual and taking corrective action for any unfavorable deviation but cost reduction does not have any specific process. Under it, the ways of reduction in have any specific process. Under it, the ways of reduction in materials, labor and other overheads are adopted.
c. Assumption: cost control assumes the existence of certain standard or norms which are not challenged whereas cost reduction assumes existence of concealed potential savings in the standard or moms which are the fore subject to constant challenge or improvement.
d. Approach: cost control lacks dynamism since it aims to attain lower possible cost under existing circumstances but cost reduction is a continuous process and recognizes no conditions as permanent.
e. Function: cost control is a preventive function. Under it, costs are optimized before they are uncured but cost reduction is a corrective function.








The best software is here you can minimize your expense
ReplyDeletehttps://www.livetecs.com
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteFree Download EBook (122 pages). So far 9500+ Downloads/Reads.
ReplyDeleteINTRODUCTION TO MODERN INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING.
#IndustrialEngineering for #SocietyProsperity through #Productivity and #CostReduction.
Industrial Engineering is concerned with #design, #installation and #improvement.
Download from:
https://academia.edu/103626052/INTRODUCTION_TO_MODERN_INDUSTRIAL_ENGINEERING_Version_3_0