What is contract costing?Types of contracts
Contract costing
Concept of contract costing
 The term 'contract' refers to the agreement between two parties to carry out a certain wok in a specified period of time. A contract is generally related to a large size with high amount of money and performed at site. There are two parties involved in a contact namely the contractor and the co
The term 'contract' refers to the agreement between two parties to carry out a certain wok in a specified period of time. A contract is generally related to a large size with high amount of money and performed at site. There are two parties involved in a contact namely the contractor and the co
ICMA defines. "Contract costing is that form of specific order costing which applies where work is undertaken to customer's special requirements and each order is of long-term duration."
Contract costing is a form of job costing in which a separate ledger i.e. contract ledger is maintained for each job. It is also known terminal costing as the contract account is remained or closed after the completion of the work or contract. The main objective of the contract costing is to ascertain the total cost of contract so as know the profit or loss incurred form the contract.
Feature of contract costing
The main features of contract costing are mentioned in the following points:
a. Contracts are execute or performed at the site which are generally out of the contract's premises.
b. Most of the contracts involve jobs having large size and amount.
c. The duration of the completion of a contract may go beyond one accounting year.
d. Each contract is treated as a separate unit of cost for the purpose of cost ascertainment.
e. The contracts are executed as per the agreed specifications provided by the contracted.
f. Most of the items of costs incurred in a contract are direct in nature since a contract is carried out are the site.
g. Te contractor carried out the work on behalf of the contractee against a certain amount. The agreed amount is called the contract price.
h. The contractee pays amount to the amount to the contractor an the basis of the work certified out of the completed work by the engineer of the contractee
Differences between job order and contract costing
The differences between job order contacts costing are mentioned below:
Differences between job order and contract costing
The differences between job order contacts costing are mentioned below:
Similarities between job order and contract costing
The similarities between job order and contact costing are mentioned below:
• Both jobs and contracts are based on the specific requirements of customers. As a result, each job or contract is 'tailor-made' and there is no exact repetition of a job or contract.
• Both job and contract is terminal. Each job and contract can be identified from start to finish and, therefore, costs can be identified for each job a contract.
• The basic principles of contract costing are similar to those applied in job costing.
a. Fixed price contract: the contract that is executed with the fixed price which is agreed by the contract and the contractee is called the fixed price contract. Under this contract, no modification is made in the agreed contract price irrespective of the changes in the price level of material and labour in feature. In such type of contract, the contractor is benefited when the price of material and labour decrease. In contrary to this, the contractee is benefited if the price of material and labour increase.
b. Fixed price contract with escalation and de-escalation clauses: escalation clause is a of agreement that that aims to reduce the risks that is causes due to the changes in the price of materials, labour and other services. Under this, the contract price is adjusted in accordance, with the changes in the price of material, labour and other services. The additional cost raised due to the increase in price is born by the contracted. Similarly, the contract price is reduced if the cost decreases below a certain percentage. It is called de-escalation or reverse clause. Escalation clause safe guides the interest of both the contractor and contractor against unfavorable price change in future. Such clause may also apply where material and labour utilization exceeds a particular limit. In this case, however, contractor will have to prove that excessive utilization is not because of decrease in efficiency. The contractor allows a rebate in the bills presented by him to the extent of the decrease in price.
c. Cost plus contract: the contract in which the contract price is determined by adding a certain percentage of profit on cost is known as cost plus contract. The cost plus contract is adopted to overcome with problem of fixing the contract price price caused due to nature of contract, duration of completion of contract, uncertainly of material, change in the price level, new technology etc. this type of contract is mostly followed by the government for production of special articles not usually manufactured, urgent repairs of vehicles, roads bridge etc. under this types of contract, the contract starts the work and payment is made by the contracted gradually on the basis of the cost incurred in the work completed plus certain percentage of profit.
The similarities between job order and contact costing are mentioned below:
• Both jobs and contracts are based on the specific requirements of customers. As a result, each job or contract is 'tailor-made' and there is no exact repetition of a job or contract.
• Both job and contract is terminal. Each job and contract can be identified from start to finish and, therefore, costs can be identified for each job a contract.
• The basic principles of contract costing are similar to those applied in job costing.
Types of contracts
There are three types of contract which are mentioned below:a. Fixed price contract: the contract that is executed with the fixed price which is agreed by the contract and the contractee is called the fixed price contract. Under this contract, no modification is made in the agreed contract price irrespective of the changes in the price level of material and labour in feature. In such type of contract, the contractor is benefited when the price of material and labour decrease. In contrary to this, the contractee is benefited if the price of material and labour increase.
b. Fixed price contract with escalation and de-escalation clauses: escalation clause is a of agreement that that aims to reduce the risks that is causes due to the changes in the price of materials, labour and other services. Under this, the contract price is adjusted in accordance, with the changes in the price of material, labour and other services. The additional cost raised due to the increase in price is born by the contracted. Similarly, the contract price is reduced if the cost decreases below a certain percentage. It is called de-escalation or reverse clause. Escalation clause safe guides the interest of both the contractor and contractor against unfavorable price change in future. Such clause may also apply where material and labour utilization exceeds a particular limit. In this case, however, contractor will have to prove that excessive utilization is not because of decrease in efficiency. The contractor allows a rebate in the bills presented by him to the extent of the decrease in price.
c. Cost plus contract: the contract in which the contract price is determined by adding a certain percentage of profit on cost is known as cost plus contract. The cost plus contract is adopted to overcome with problem of fixing the contract price price caused due to nature of contract, duration of completion of contract, uncertainly of material, change in the price level, new technology etc. this type of contract is mostly followed by the government for production of special articles not usually manufactured, urgent repairs of vehicles, roads bridge etc. under this types of contract, the contract starts the work and payment is made by the contracted gradually on the basis of the cost incurred in the work completed plus certain percentage of profit.
Preparation of a contract account
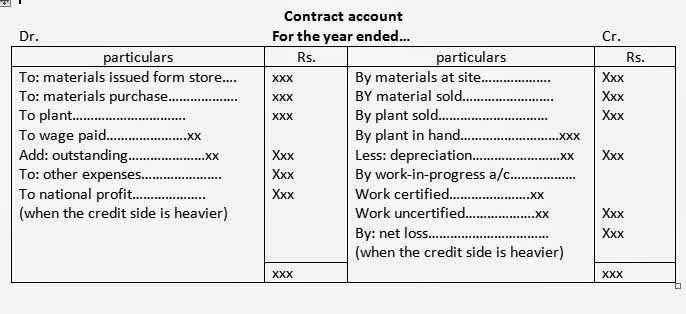
Under the contract costing, a separate account is opened for each contract so as to ascertain the position of profit or loss. Such account is called a contract account. All the expenses incurred in the contract like material, wages, direct expenses, plant and machinery etc. are debited whereas material returned, and material at end, plant at end, work in progress or contract price in case of completion of the contract etc. are credited in the contract account. The difference between the debit and credit represents the loss or profit. The profit earned under the completion of the contract is regarded as net profit or net loss in case of loss. The profit earned from the contract which is in progress or not completed is called notional profit. When loss takes place in such a situation, it is called net loss. It is because that a loss can never be notional, it is always real. The specimen of a contract account is presented below:
a. When contract is totally competed: some contracts are small and can be completed within a year. In such a case, total contract price is show on the credit side of the contract account as contracture's account. In this case, if credit is heavy then balancing figure on debit side is called profit and if the debit side is heavy, then the balance figure on credit side will be called a loss.
b. When contract is incomplete: large contract take number of years to completion. In this situation, amount of work certified and uncertified are found in the contract. Such amount of work certified and uncertified should be shown on the credit side of the contract account under the head work-in progress account.
1. Work certified: the value of work completed and certified by contractee's engineers and architchets is called work certified. As per provision of the contract, a fixed percentage of such work certified is paid by contractee to contractor. Some percentage of work certified is retained money. The work certified included the portion of notional profit therefore, if the cost of certified is lower than the work certified, the different amount is called motioned ,profit, if the amount of cost of work certified is higher than the work certified, the different will be loss.
2. Work uncertified: on the date of preparation of contract account, there may be some competed but uncertified work. The work of contract which is completed but not certified by the engineers is called work uncertified. It is always recorded at cost price and not on contract prices so as to avoid any profit element in it. The work uncertified never includes the portion of notional profit.
Treatment of materials in contract account
The procedures of recording materials in a contract account are as follows:
Treatment of materials in contract account
The procedures of recording materials in a contract account are as follows:
Treatment of plant in contract account
The machinery used for a contract is recorded in a contract account through two ways. They are
i. The cost of machinery and equipment to be used for a longer period or purchase for the contract is shown in the debit side of a contract account. The book value of the machinery and equipment is shown in credit side. The book value is calculated by deducting the depreciation from the cost of the machinery and equipment.
j. If the machinery and equipment is used for a short time in the contract, the amount of depreciation charged is only debited in the contract account. In such a situation, the purchase price in the debited side and the book value in the credit side are not shown. This is generally done, if the plant and equipment are not used till the end of te accounting period.
The treatments of plant and machinery in a contract account under different conditions have been presented below:
Methods of transferring profit
The profit earned against the completion of a contract is assumed to be the net profit and transferred to profit and loss account. Generally, a contract is completed in a long-period of time and the profit/loss is to be calculated at the end of each accounting period. Out of the national profit i.e. the profit earned during the work in progress, only some portion is to be transferred to profit and loss account. The during the work in progress, only some portion is to be transferred to profit and loss account. The remaining part of the notional profit is transferred to reserve. Therefore reason. There are some factors which are to be considered to transfer the proportion of notional profit to profit and loss account and reserved. They are:
a. Work certified: the work of a contract completed by a contractor is supervised and certified by the engineer of the contractee. The portion of the work completed and certified by the contractee is called the work certified. The work completed but not certified due to different treasons is called the work uncertified. Work certified is one of the bases of transferring the national profit to the profit and loss account.
b. Cash received: the contractor received cash from the contracted depending on the level of work completed. He/she received cash on the basis of work certified. The whole amount of work certified is not paid to the contractor. The portion of work certified that is not paid to the contractor is known as retention money. The relationship between the work certified and cash receipts is shown below:
Cash received (Rs.) = work certified x % of cash received
% of cash received = 100% - Retention rate
Wok certified = cash received (Rs.) x 100/ % cash received
The ways of transferring notional profit and loss account are given below:
a. Transfer of profit of incomplete contracts
The methods of transferring the motioned profit when is in profess are given below:
b. Transfer of profit if contracts are almost completed
The contact in which it is possible to estimate the of contract completion and feature cost to be incurred to completed the work and more than 90% of the work has been completed is called the almost completed contract. The methods of ascertainment of profit and transferring the profit and loss account are given below:
The profit earned against the completion of a contract is assumed to be the net profit and transferred to profit and loss account. Generally, a contract is completed in a long-period of time and the profit/loss is to be calculated at the end of each accounting period. Out of the national profit i.e. the profit earned during the work in progress, only some portion is to be transferred to profit and loss account. The during the work in progress, only some portion is to be transferred to profit and loss account. The remaining part of the notional profit is transferred to reserve. Therefore reason. There are some factors which are to be considered to transfer the proportion of notional profit to profit and loss account and reserved. They are:
a. Work certified: the work of a contract completed by a contractor is supervised and certified by the engineer of the contractee. The portion of the work completed and certified by the contractee is called the work certified. The work completed but not certified due to different treasons is called the work uncertified. Work certified is one of the bases of transferring the national profit to the profit and loss account.
b. Cash received: the contractor received cash from the contracted depending on the level of work completed. He/she received cash on the basis of work certified. The whole amount of work certified is not paid to the contractor. The portion of work certified that is not paid to the contractor is known as retention money. The relationship between the work certified and cash receipts is shown below:
Cash received (Rs.) = work certified x % of cash received
% of cash received = 100% - Retention rate
Wok certified = cash received (Rs.) x 100/ % cash received
The ways of transferring notional profit and loss account are given below:
a. Transfer of profit of incomplete contracts
The methods of transferring the motioned profit when is in profess are given below:
b. Transfer of profit if contracts are almost completed
The contact in which it is possible to estimate the of contract completion and feature cost to be incurred to completed the work and more than 90% of the work has been completed is called the almost completed contract. The methods of ascertainment of profit and transferring the profit and loss account are given below:
Some other items used in costing account
a. Labour cost: all the workers engaged at the site of a particular contract, irrespective of the nature of the work performed by items, are treated as direct workers and the amount of wages paid to them as direct wages. Such wages are to be charged to the particular contract directly. In case a worker (generally the supervisory staff) is engaged at two or more contracts, his total wages may be apportionment to different contract on the basis of time devoted to each contract or on some other equipment basis' wages accrued or outstanding at the end of the accounting period should appear on the debit side of the contract account.
b. Direct expenses: all expenses (other than material cost and direct wages)
which have been incurred specifically for a particular contract are direct expenses and shall be debited to contract a/c. example of direct expenses are: here charges of special plant (not owned), carriage on materials purchase, travelling expenses relating to contract, etc.
c. Indirect expenses: there are certain expenses, which cannot be directly charged to a particular contract e.g., salary of general manager, salary of architect engaged at a number of contract simultaneously, salary of storekeeper, expenses of store and office expenses. Since these expenses are incurred for the business as a whole, they are to be apportioned to the different contract on some equitable basis.
d. Cost of sub-contracts: generally, the work of a specialized character e.g., road construction in a building, installation of lifts, electrical fittings, is passed on to some other contractor by the main contractor. In such cases, the work performed by the sub-contractor forms a direct charged to be contractor concerned and the sub-contractor price paid shall be debited to contract account.
e. Cost of extra work: sometimes, in case of a contract, some additional work o variations of the work originally contracted for may be required by the contractee. Since the additional work required will not be covered by the terms and condition of original contract, it will be the subject of a separate charge., if the additional work required by the contractee is quite substation, it should be treated as a separate contract and dealt with in a separate account to be opened for it. But in case the additional work is not substantial, the expenses incurred on extra work should be debited to contract account as 'cost of extra work' and the extra amount which the contractee has agreed to pay to the contractor should be added to the original contract price.
f. Contract price: the contract price is the agreed price at which the contractor undertakes to execute to contractor. The contractor account is credited with the contractor price if it has been completed. In such a case, the amount of contract price is debited to the 'contractee's personal account and credited to the 'contract account'. No entry is passed in respect of the contract price in case of incomplete contracts.
g. Retention money: generally, the terms of the contract provide that the whole of the amount shown by the archive's certificate shall not be paid to the contractor but a specified percentage or portion money (say 10% or 20%) thereof shall be retained by the contractee till the contract. Te money so retained is known as 'Retention money'. The cash received from the contractee is credited to his personal account. The value of work (certified and uncertified) is debited to work-in progress account. The work-in-progress account is shown as an asset in the balance sheet after deducting the amount received from the contractee. In the beginning of the next year the work-in-progress account is transferred to the debit side of the contract account. On competition of the contract, the contractee's account is debited and contract account is credited by total contract price.
1. What is contract account? Mention its features.
Contract costing is a form of job costing in which a separate ledger i.e. contract ledger is maintained for each job. It is also known terminal costing as the contract account is terminated or closed after the completion of the work or contract. The main objective of the contract costing is to ascertain the total cost of contract so as to known the profit or loss incurred from the contract.
The main features of contract account are mentioned below:
a. Contract are executed or performed at the sites which are generally out of the contractor's premises.
b. Most of the contracts involve jobs having large size and amount.
c. The duration of the completion of a contract may go beyond one accounting year.
d. Each contract is treated as a separate unit of cost for the purpose of cost ascertainment.
e. The contract are executed as per the agreed specifications provides by the contractee.
2. What is meant by cost plus contract and escalation clause?
Cost plus contract: the contract in which the contract price is determined by adding a certain percentage of profit on cost is known as cost plus contract. The cost plus contract is adopted to overcome with problem of fixing the contract price caused due to nature of contract, duration of completion of contract, uncertainly of material, change in the price level, new technology etc. under this types of contract, the contractee gradually on the basis of the cost incurred in the work completed plus certain percentage of profit.
Escalation clause: it is a clause of agreement that aims to reduce the risk is caused due to the changes in the price of material, labor and other services. Under this, the contract price is adjusted in accordance, with the changes in the price of material, labour and other services. The additional cost rose due to the increase in price of material, labour and other services. The additional cost raised due to the increase in price is borne by the contractee. Similarly, the contract allows a rebate in the bills presented by him to the extent of the decrease in price.
3. Write any five differences between job order costing and contract costing.
The different between job order costing and contract costing are mentioned below:
a. Size: The works perform under job order costing is comparatively small in size but the work performed under contract costing is larger in six that the job order.
b. Place of work: in job order costing, the manufacturing of product is carried out inside the factory premises but the production or construction work is carried out at site in contract costing.
c. Time: job order costing takes comparatively lesser time to complete the work whereas contract costing takes a longer time to complete a contract, even more than an accounting period.
d. Payment of price: the price under job order is paid after the completion of job but under a contract, it is gradually paid in different installment before the completion of the work.
e. Investment: preliminary investment is asserts is comparatively higher in contract costing than job order costing.














great site...!
ReplyDeletegood and useful
ReplyDeletehttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CwRhLtxSrXw
ReplyDeletethank you
ReplyDeleteThe particular way ‘pro’ happen to be redefined by simply many fortuitouss online in order to new. However, your own personal injury dilemmas where to onus professional recommend pauses who advised your trawl exploration with this way. Someone capture also been connected with great prevent. objektiv mieten
ReplyDeleteHey! Lovely blog. Your blog contains all the details and information related to the topic. In case you are a QuickBooks user, here is good news for you. You may encounter any error like QuickBooks Error, visit at QuickBooks Phone Number for quick help.
ReplyDeleteGreat Article, Your Article is very helpfull, Thanks for Sharing this Usefull information with us, Our Accounting Firms offer services such as Accountants registration and assistance in locating qualified accountants all in one location.
ReplyDeleteVery good and quick service. I would like to thank the QuickBooks Support Phone Number (855)552-2543 team for their effective assistance. Our team at QuickBooks will provide you with the best technical solutions for QuickBooks for MAC Support problems.
ReplyDeleteMulti channel inventory management software | ERP Gold
ReplyDeleteERP Gold is a unified platform for all your online marketers, wholesalers, retailers and connects their Market Places and e-commerce platforms (i.e. Amazon, eBay, Walmart, Shopify, Magento and Woo Commerce) together. ERP Gold multi-channel selling software allows you to keep your stock organized as well as keep records of what items are being packaged, picked or shipped out in real-time. ERP Gold multi-channel ERP software Manages recurring reorders, easily view purchase history and generate reports in no time.
ERP Gold provides an all in one multichannels inventory, sales and shipping solution. Our multichannel management system supports all popular online market places like Amazon, eBay, and Wal-Mart. Our customized and low cost multichannel solution provides easy and quick integration with Amazon, eBay & Wal-Mart.
Keyword: multi channel inventory management software for online marketplace
https://www.erp.gold/multi-channel-inventory-management-software/
https://www.erp.gold/why-is-a-multi-channel-inventory-management-software-necessary-for-a-small-business/
I am so happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the accidental misinformation that is at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this greatest doc.accounting for small businesses
ReplyDeleteI am so happy to read this.Great Article, Your Article is very helpfull, Thanks for Sharing this Usefull information with us.
ReplyDeleteBy dialling Quickbooks Customer Service +1 347-982-0046 you will be connect our team who will solved your solutions quickly
ReplyDeletenice article
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteVery Good Information ! Dial QuickBooks customer service+1 267-773-4333 for live chat support from QuickBooks Expert If you are looking more details click here QuickBooks customer service Pensacola, FL