What is Cost controlling accounting?
Meaning of cost control accounting
Costing department is responsible for the maintenance of cost accounting and preparations of cost reports and other statements. Cost accounting is essentially maintained on the principle of double entry book-keeping system. There are two bases of maintaining cost accounts:
a. In depended or non-integrated accounting and
b. Integral or integrated cost accounting
When accounting is maintained by integrating the cost and financial accounting, the systems is called integrated or integral accounting. On the other hand, if they are maintained separately, it is called non integrated accounting. In other words, under the in depended or non-integrated accounting systems, a separate set of costing books is maintained along with the books of accounts under financial accounting. Under it, the cost ledgers are independent of the financial ledger. On the other, an integral accounting represents a system under which both the cost and financial accounts are merged into a composite system. The accounting department maintains all types of accounts, i.e. personal, real and nominal, through to cost department is primarily concerned with the income and expenditure of the enterprises.
Non-inter-graded or independent accounting
Concept f non-integrated accounting
Under non-integrated accounting systems, the records of cost and financial transactions are made separately and a separated set of costing books are maintained along with the financial books of accounts.
Chartered institute of management accountants (CIMA), London defines integral account as "a systems in which cost accounts are district from financial accounts, the two sets of account being kept continuously in agreement or readily recognizable."
From the above, it is clear that non integrated accounting is a system in which the cost and financial accounting are maintained separately and independently.
Advantages of non-integrated accounting
The following are the advantages of non-integrated accounting:
• It helps managerial analysis by presenting the detailed information constrained in different subsidiary ledger by control accounts.
• It facilitates the division of labour in accounting work.
• It helps to prepare profit and loss account and balance sheet promptly.
• It also assists in the smooth operation of internal check system in an organization.
• It also acts as a base reconciliation of profit between cost and financial account.
Cost ledgers
Cost ledgers are the principle ledgers maintained by cost department. It contain all impersonal accounts including overhead accounts such as factory overhead, administrative overhead, selling and distribution overhead etc. they are classified by the various production and service departments or other cost enters. The balances of such accounts are transferred to control accounts.
The following are the main objective of maintaining cost ledgers.
a. To maintain cost accounts properly.
b. To analyze, control and compare cost.
c. To act as a cost control tool in case the standard costing is in vogue. Costs are collected and classified on department and product or process-wise. These are compared with the standards, variances computed and remedial measures are taken by the management.
d. To control materials, labour and overhead.
e. To help in determining the closing stocks, work-in-progress without any delay and enable the prompt preparations of periodical profit and loss account and other statements.
f. To maintain accounts relating to production such as fixed and variable expenses, controllable and uncontrollable and normal abnormal wastage.
In addition to cost ledger, following other ledger are also maintained under non-integral costing systems by large organizations.
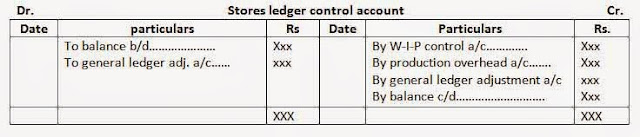
a. Stores ledger: it contains all accounts of individual items of raw materials, components and consumable stores. In cost ledger a stores ledger control a/c is opened to represent the stores ledger in total.
b. Work-in-progress ledger: work-in-progress control a/c is maintained in the cost ledger which represents the work-in-progress ledger a/c in total. In this ledger, accounts of all jobs pending on the floor are maintained, each job is allocated a codes no. and a separate account is opened for each job.
c. Finished stock ledger control a/c: finished stock ledger control a/c is maintained in cost ledger to represent finished stock in total. It constrains items-wise accounts in respect of finished goods interred for sale.
Journal entries
Under cost ledger accounting system the cost control accounts are kept separated from the financial ledgers. These control accounts are maintained on the principles of double entry book-keeping. Under this the following journal entries are passed according to double entry systems.
Control accounts
Under non intergraded accounting ledger are prepared for recording numerous transactions instead of posting them into general ledger. The total of all these accounts in the subsidiary ledger are posted in total at the end of the period to control accounts in the cost ledger. These are total accounts kept in the cost ledger. These accounts form the medium of control over all the expenditures chargeable in jobs and which facilities automatic means recording cost with the financial books.
The main purposes of cost control accounts are:
h. To summaries the detailed information contained in the subsidiary ledger and provides the summary to the management for policy formulation.
i. To check the all the expenditures name accounted for in the cost accounts with double entry system.
j. To facilitate compilation of financial accounts and reconciliation with cost accounts.
k. To act as a means of preparing profit and loss accounts and balance sheets and other cost statements at any interval, say monthly, quietly etc.
l. To provide an effective system of interest check since there is cross-checking of work done by difference person. This lead to greater accrued of records.
Following are the importance control accounts:
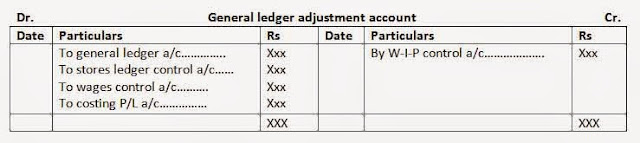
a. General ledger adjustment a/c or cost ledger control a/c: general ledger adjustment account is maintained to make cost ledger self balancing. In this account, all the entries in respect of items of income or expenditure extracted from the financial accounts are posted. In effect, the cost books to the financial book, e.g., cost of capital work performance by the factory, will be bettered in this account. However, no entry is required if a transaction is of the internal natures, i.e., transfer from stores ledger control account to work-in-progress account. It must be noted that no entry should be made directly from the financial books to the cost books, rather entries must be passed through the general ledger adjustment a/c. the balance on this account represented the total of all balances of to importance accounts. The format of general ledgers adjustment account is as below:
b. Stores ledger control a/c: in stores control account, receipts and issues of materials are recorded from goods received notes and stores requisitions respectively. The balances of this account represent the total balance of stores which should agree with the aggregate balance of to work-in-progress account and notes to the stores ledger control account. In short, stores ledger control account represented the stores ledger in total.
c. Work-in-progress control a/c: work-in-progress control account indicates to total amount of work-in-progress at any time. This account is debited with opening with the balance of work-in-progress at any time. This account is debited with operating balance of work-in-progress, if any, direct materials, direct labour costs, direct expenses, production overhead recovered and is credited with the actual or predetermined cost of finished products transferred to finished goods stores. Materials returns transfer and abnormal time costs are also credited to the respective jobs. The balance of this account shows the total balance of jobs, which are in progress as per individual jobs accounts. This account shows the work-in-progress ledger accounts in total. The main sources of entries for this account are goods received notes, materials requisitions notes transfer notes, bill of materials, wages abstracts, etc.
d. Wages control account: wages control account pertains to all types of wages and labour costs incurred. In fact, this accounts act as a clearing hour for wages incurred and absorbed. Direct wages are transferred to work-in-progress a/c and indirect to respective overhead control accounts.
Production or manufacturing overhead account: production or manufacturing overhead account contains the factory expenses. It is debited with indirect material cost, indirect wages and indirect expenses and credited with the amount of overhead recovered. Overhead allocated to work-in-progress are carried over to the next period. The balance in the control a/c represented under-or over absorption and is transferred to costing profit loss a/c.
f. Administration overhead a/c: administration overhead account is debited with the administration costs and credited with the overhead recovered. Any balance, in this account, is transferred to costing profit and loss a/c.
j. Costing profit and loss a/c: costing profit and loss account recorded the transfer of the account in respect of under-or over-recovered overhead, the sale value of goods sold and balances from cost of sale account. The accounts is also credited or debited with the abnormal losses or gains. The closing balance represented profit or loss and is reconciled with the profit or loss as per financial profit and loss account.
Integrated accounting
Concept of integrated accounting
The accounting systems under which the recording of the cost and financial accounts are maintained in an integrated system is called the integrated accounting. Under it, separate accounts are not credited for the cost financial transactions. This is mainly followed to gain economy and remove duplication of recordings. The subsidiary and control ledger prepared under integrated accounting are mentioned below:
c. Work-in-progress control a/c: work-in-progress control account indicates to total amount of work-in-progress at any time. This account is debited with opening with the balance of work-in-progress at any time. This account is debited with operating balance of work-in-progress, if any, direct materials, direct labour costs, direct expenses, production overhead recovered and is credited with the actual or predetermined cost of finished products transferred to finished goods stores. Materials returns transfer and abnormal time costs are also credited to the respective jobs. The balance of this account shows the total balance of jobs, which are in progress as per individual jobs accounts. This account shows the work-in-progress ledger accounts in total. The main sources of entries for this account are goods received notes, materials requisitions notes transfer notes, bill of materials, wages abstracts, etc.
d. Wages control account: wages control account pertains to all types of wages and labour costs incurred. In fact, this accounts act as a clearing hour for wages incurred and absorbed. Direct wages are transferred to work-in-progress a/c and indirect to respective overhead control accounts.
Production or manufacturing overhead account: production or manufacturing overhead account contains the factory expenses. It is debited with indirect material cost, indirect wages and indirect expenses and credited with the amount of overhead recovered. Overhead allocated to work-in-progress are carried over to the next period. The balance in the control a/c represented under-or over absorption and is transferred to costing profit loss a/c.
f. Administration overhead a/c: administration overhead account is debited with the administration costs and credited with the overhead recovered. Any balance, in this account, is transferred to costing profit and loss a/c.
g. Selling and distributions overhead a/c: selling and distributions costs are divided to selling and distributions overhead account and credited with the amount of overhead recovered, the balance, if any, is transferred to costing profit and loss a/c.
h. Finished goods ledger control a/c: finished goods ledger control account is also known as stock ledger control account. The total value of finished goods in stock is represented in this account. This account is debited with operating balance of finished goods and the cost of finished goods transferred from work-in-progress control a.c. it is credited with cost of sales and the balance represented the amount of unsold stock in business.
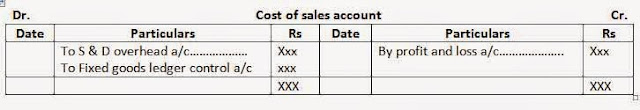
i. Cost of sales a/c: cost of sales account records the actual sales made and profit earned thereon. This account is debited with the cost of goods sold, selling and distribution overhead, recovered and is closed by transfer to costing profit and loss a/c.j. Costing profit and loss a/c: costing profit and loss account recorded the transfer of the account in respect of under-or over-recovered overhead, the sale value of goods sold and balances from cost of sale account. The accounts is also credited or debited with the abnormal losses or gains. The closing balance represented profit or loss and is reconciled with the profit or loss as per financial profit and loss account.
Integrated accounting
Concept of integrated accounting
The accounting systems under which the recording of the cost and financial accounts are maintained in an integrated system is called the integrated accounting. Under it, separate accounts are not credited for the cost financial transactions. This is mainly followed to gain economy and remove duplication of recordings. The subsidiary and control ledger prepared under integrated accounting are mentioned below:
Under integrated accounting profit or loss is calculated by making profit and loss account only at the end of the accounting period. Therefore, it is not necessary to prepare a cost reconciliation statement to reconcile the profit as per financial account and cost account. The integrated accounting also helps in bringing co-ordination between the activities between costing and financial department.
Difference between non-integrated and integrated accounting cost control accounting
The differences between the integrated and non integrated accounting are as follows.



















Business organizations needs to write and prepare ledger account wherein all the transactions of are recorded permanently under different heads of accounts.
ReplyDeleteI am a regular user of your post, this one also was very interesting and well written. keep sharing the great work
ReplyDeletevat return service In London