Cash flow statement
What is Cash flow statement?Importance of cash flow statement & Difference between cash flow statement and funds flow statement
What is Cash flow statement?Importance of cash flow statement & Cash flow statement under direct method,Cash flow statement under indirect method
What is Cash flow statement?Importance of cash flow statement & Difference between cash flow statement and funds flow statement
What is Cash flow statement?Importance of cash flow statement & Cash flow statement under direct method,Cash flow statement under indirect method
Introduction
Meaning of cash flow statement
The purposes of cash flow statement are as below:
i. To provide information about the cash inflows and cash outflows from operating, financing and investing activities of the firm.
ii. To show the impact of the operating, financing and investing activities on cash resources
iii. To tell how much cash came in during the period, how much cash went out and what the net cash flow was during the period.
iv. To explain the cause for changes in the cash balance.
v. To identify the financial needs and help in forecasting future cash flows
Importance of cash flow statement
The importance of cash flow statement is presented as below:
The different between funds flow statement and cash flow statement is presented as below:
Basis of difference Funds flow statement Cash flow statement
Concept of operating activities
Balance sheet, income statement and funds flow statement are the three financial statements, which are very closely linked, and they play and important role in providing financial insights into a firm. A balance sheet reports the cash balance at the end of the period. By examining two consecutive balance sheets, we can tell whether cash is increased or decreased during a
particular period. However, the balance sheet cannot indicate why the cash balance changed. The income statement report revenues, expenses and net income. These items provide information about the resource generating capacity and profitability, but income statement itself cannot tell why cash increased or decreased. Similarly, funds flow statement helps to explain how a firm acquired its money and how it was spent. But this statement fails to provide information about the causes of variation in cash balance. In other words, business organizations engage in different activities such as operating activities, financing activities and investing activities. Therefore, cash flow statement is prepared to explain the cash inflows and cash outflows associated with operating, financing and investing activities of the firm.Meaning of cash flow statement
The cash flow statement reports the firm's cash flows during a period, outlining where cash generated from and where it was spent. In other words, cash flow statement is an indicator of the amount of cash receipts and the amount of cash payments or disbursements during a specified period. Opening, financing and investing activities are the major business activities that result in either a net cash inflow or a net cash outflow. The cash flow statement shows the net increase or decrease in cash during a particular time period and explains the causes for the changes in the cash balance.
Natural of business activities
In this way, cash flow statement is an important to the other major financial statements. Cash flow statement furnishes the important cash activities of an enterprise. Cash flow statement summaries the operating, investing and financing activities of a business organization, reports the changes in cash over a period of time and explains the causes of changes.
Objective of cash flow statementThe purposes of cash flow statement are as below:
i. To provide information about the cash inflows and cash outflows from operating, financing and investing activities of the firm.
ii. To show the impact of the operating, financing and investing activities on cash resources
iii. To tell how much cash came in during the period, how much cash went out and what the net cash flow was during the period.
iv. To explain the cause for changes in the cash balance.
v. To identify the financial needs and help in forecasting future cash flows
Importance of cash flow statement
The importance of cash flow statement is presented as below:
i. Cash flow statement furnishes the important cash activities of an enterprise and summaries the performance on cash basis. Income statement is prepared on accrual basis; therefore, cash flow statement is considered a better indicator of future cash inflows and outflows than income statement.
ii. Cash flow statement discloses the movement of internal fund related with operating activities of an enterprise. Therefore, this statement is more appropriate for internal financial planning, controlling and decision-making.
iii. Cash flow statement is a critical disclose to company's investors and creditors. Company's investors and creditors focus on cash flow from operation rather than net income because they care about the company's ability to pay bills rather profit earned.
iv. Cash flow statement provides various groups of users a valuable starting point for evaluating the company's financial health. These groups pay special attention to the cash flow adequacy ratio and cash flow per share, which are based on net cash generated by a firm during a particular period of time.
v. Cash flow statement is useful in making internal as well as external investment and financing decision such as project expansion, replacement of projects, repayment short term and long term debt etc.
Difference between cash flow statement and funds flow statementThe different between funds flow statement and cash flow statement is presented as below:
Basis of difference Funds flow statement Cash flow statement
Objectives The objectives of funds flow statement are to disclose the cause of changes in working capital. The objectives of cash flow statement are to disclose the causes of changes in cash and cash equivalents.
Basis Fund flow statement is based on accrual bases of accounting. Cash flow statement is bases on cash basis.
Time range Funds flow statement is prepared for the long range financial planning. Cash flow statement is useful for short range financial planning.
coverage Funds flow statement contains all the components of working capital. Cash flow statement is confined to cash and cash equivalents only which is just one of the components of working capital.
Cash flow from major business activities
Business activities are divided into three sections i.e. cash flow operating activities, cash flows from investing activities and cash flows from financing activities for the purpose of preparing cash flow statement. These activities are presented in exhibit 2.
Cash flow operating activitiesConcept of operating activities
Operating activities is convened with the day-to-day business operations. Cash flow from operating activities is any cash transaction related to the firms' operating business, which is responsible for most of the profit earned or loss, suffered. Operating activities usually involve producing and delivering good and rendering services. Sales or services revenue is the major source of cash inflow under operating activities. Cost of purchases and cost of goods sold, payment of wages, salaries, rent, interest, tax and other expenses are the major sector sector of cash outflow. Cash flow from operations is the major means of generating cash. Cash from operations shows the extent to which day-to-day operating activities have generated more cash than the cash, which has been used.
The cash flow from operating activities is basically related with revenue, cash expenses and changes in current assets and current liabilities. The cash inflow and outflow from this activity has been presented in following exhibit 3.
Cash inflow and outflow under operating activities
Cash inflow Cash outflow
From trading account Sales revenue service revenue Cost of goods sold, wages and manufacturing expenses
From profit & loss account Sundry operating income received such as commission, interest, rent, dividend etc. receive, bad debt recovered Operating expenses (cash items only) such as office expenses, selling expenses, distribution expenses, interest, tax, etc.
From asset side of balance Decrease in all current assets except cash & cash equivalents. Increase in all current assets accepts cash and cash equivalents.
From liability side of balance sheet Increase in all current liabilities Deceased in all current liabilities
According to the clause 03 and section 6 of Nepal accounting standard (NAS-03 SEC-6). Following items are the examples of cash flows relating to operating activities:
i. Cash receipts from the sales of goods and by rendering services.
ii. Cash receipts from fee, commission, royalties and other services.
iii. Cash payment to suppliers for good and provides of services.
iv. Cash paid to employees.
v. Cash receipts and cash payments of and insurance enterprise for premium and claims, announcing and other benefits.
vi. Cash payment or refund of income taxes unless they can be specially identified with financing and investing, and
vii. Cash receipts and payment from contacts held for dealing or trading purchase.
Cash and cash equivalents are not included in the cash flow from operating activities. In other words, cash and cash equivalents are adjusted at the end of cash flow statement i.e. their opening balance are added with the net changes in cash balance to determine their ending balance.
Determination of cash from operating activities under direct method
Net cash flow operating activities can be ascertained either by using direct method or indirect method. Under direct method, cash from operating activities is determined by deducting all cash expenses from the revenue generated in cash. Under indirect method, cash from operating activities is calculated on the basis of net income, non-operating and non-cash items and changes in current assets and current liabilities. Both methods are equally applicable, however, Nepal accounting standard emphasis direct method. Accounting to be clause 03 and report cash flow from operating activities using the direct method.
Cash collection from customers
Cash collection from customers includes the amount of cash sales and cash received from customers or credit sales. The sales reported by income statement are the combination of cash and credit sales. The cash generated through cash sales cash collection from credited sales is determined with the help of changes in the customer's account of bad debt written balance sheet. The amount of cash received is also affected by the amount of bad debt written off, bad debt recovered and discount allowed to customers. Following points are important to note while calculating cash collection form customers.
• An increase in debtors/accounts receivable/bills receivable account represents increase in credit sales, which reduces cash collection.
• A decrease in debtors/account receivable/biils receivable account represents cash collection from customers.
• An increase in provision for doubtful debt and provision for discount on debtors increase cash inflow and decrease in these accounts represent cash outflow.
• Bad debt recovered is a source of cash and discount allowed to customers is an application of cash.
Cash paid to suppliers
The major area of cash outflow under operating activities is the purchases of merchandise or goods purchase for the purpose of selling or manufacturing finished goods. Merchandise can be purchase either on cash or on credit. Sundry creditors, bill payable, accounts payable, suppliers account etc. are the account which show the condition of credit purchase during a particular period of time. The purchase or cost of goods sold shown by income statement represent both cash and credit purchase and cash paid to suppliers is determined with the help of cost of goods sold and changes is suppliers account and the position of inventory of merchandisers. Following points are importance to note while calculating cash paid to suppliers for the purchases of merchandise:
• An increase in creditors/accounts payable/bills payable account represents the credit purchase which decreases the cash outflow.
• An increase in ivestory represents purchase and decrease in inventory represents sales of merchandise.
• A decrease in creditors/account payable/bills payable account represent cash paid to suppliers which increase the cash outflow.
• Discount received from suppliers reduces the cash outflow
Cash paid to employees and for other expenses
Wages, salaries, rent general office expenses, selling and distribution expenses, depreciation are the example of operating expenses. Out of these expenses, depreciation is non-cash expenses. Income statement includes different types of operating and non-operating expenses, but only cash operating expenses are taken into account while determining cash paid to employees and for other expenses. Different types of operating and non-operating expenses expense losses as follows:
Interest payment
Interest on different types of loan is included either under operating activities or under financing activities. In the absence of any information, interest paid is considered as operating expenses and should be included under the operating section of cash flow statement. However the provision regarding the treatment of interest paid under Nepal accounting standard (NAS 03 sec 31, 32, 33 and 34) are as below:
• Cash flow from interest and dividend should be disclosed separately. Each should be classified in a consistent manner from period to period, operating, investing or financing activities.
• The total amount of interest paid during a period is disclosed in the cash flow statement whether it has been recognized as an expense in the income statement or capitalized.
• Interest paid is usually classified as operating cash flow flow a financing institution. However, there is no consensus on the classification for other enterprises. Interest paid may include under financing activities because interest paid is a cost of financing.
Tax payment
Tax paid is treated as cash outflow operating revenue. The amount of tax paid is determined on the basis of tax expense of the current year and position of outstanding tax. The method of ascertaining tax paid is as below:
Interest and dividend received
The provision regarding the treatment of interest and dividend received has been explained in section 31, 32, 33 and 34 under Nepal accounting standard (NAS-03). Cash flow from interest and dividend received should be disclosed separately. Each should be classified in a consistent manner from period to period, operating, investing or financing activities. Interest and dividend received are usually classified as operating cash inflow because they enter into the determination of net income or loss. Interest and dividend received may include under investing activities because they are treated as return on investment or shares, debentures and other assets. Interest and dividend is computed as below:
Cash from extra ordinary items
Cash sales and cash collection from customers, cash purchase and cash paid to suppliers, cash paid to employees and for other expenses, interest and dividend received or paid and tax paid are the normal or ordinary items relating with the operating activities. Beside these ordinary items, they are some other items concerned received with the operational cash flow of a business such as short term borrowing, compensation received from insurance companies etc. increase in the balance of extra ordinary items is treated as source or cash inflow and decrease in their balance is considered as cash outflow.
Cash and cash equivalent assets
All current assets and current liabilities are included under operating activities except cash and cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include cash in hand, cash at bank and any cash invested in short-term and highly liquid financing instruments. Generally, marketable securities cash as treasury bulls, commercial paper, and money market funds are also the examples of cash equivalents. If there are more than one item of cash and cash equivalents in the balance sheet, their opening and closing balance is computed as below:
Determination of cash from operating activities under indirect method
Under indirect method, cash flow from operating activities is determined on the basis of the following information:
• Net income or loss
• Non-cash expenses and losses, non-operating expenses, losses and amortizations
• Non-operating incomes and gain
• Changes in current assets (except cash & equivalents)
• Changes in current liabilities
Cash flow from investing activities
Cash flow from investing activities is the second part of cash flow statements. Investing activities are related with the purchases and sales of non-current assets such as plant and machinery, land and building, furniture and fixture etc. investing activities also include lending money and the purchase or sales of investment in securities activities explain the changes in cash position between to balance sheet dates due to the buying or selling of non-current assets. The cash inflows and outflows related with investing activities can be presented as below:
Cash flow from financing activities
The financing activates section of the cash flow statement shows the sources of fund generated through owner's capital and borrowed capital. Financing activities also include the repayment of debt and payment of cash dividend to shareholders. The major financing activities of a firm and impact of these activities on cash flow stream are presented as below:
Preparation of cash flow statement
Cash flow statement is prepared by combining the cash flows from operating activities investing activities and financing and financing activities. The main steps involved in the preparation of cash flow statement are presented in the following:
Cash flow statement under direct method
Combining the cash flows generated from operating, investing and financing activities, cash flow statement is prepared to show the net change on cash balance during a particular period. It can be prepared according to the direct direct or indirect method; the specimen of cash flow statement under direct method is as below:
Cash flow statement under indirect method
Cash flow statement can be prepared by using indirect method also. The difference between direct method and indirect method is only cash flows from operating activities. Cash flow from investing and financing activities are similar under direct and indirect methods. The format of cash flow statement under indirect method is as below:
Read More.....
Cash inflow and outflow under operating activities
Cash inflow Cash outflow
From trading account Sales revenue service revenue Cost of goods sold, wages and manufacturing expenses
From profit & loss account Sundry operating income received such as commission, interest, rent, dividend etc. receive, bad debt recovered Operating expenses (cash items only) such as office expenses, selling expenses, distribution expenses, interest, tax, etc.
From asset side of balance Decrease in all current assets except cash & cash equivalents. Increase in all current assets accepts cash and cash equivalents.
From liability side of balance sheet Increase in all current liabilities Deceased in all current liabilities
According to the clause 03 and section 6 of Nepal accounting standard (NAS-03 SEC-6). Following items are the examples of cash flows relating to operating activities:
i. Cash receipts from the sales of goods and by rendering services.
ii. Cash receipts from fee, commission, royalties and other services.
iii. Cash payment to suppliers for good and provides of services.
iv. Cash paid to employees.
v. Cash receipts and cash payments of and insurance enterprise for premium and claims, announcing and other benefits.
vi. Cash payment or refund of income taxes unless they can be specially identified with financing and investing, and
vii. Cash receipts and payment from contacts held for dealing or trading purchase.
Cash and cash equivalents are not included in the cash flow from operating activities. In other words, cash and cash equivalents are adjusted at the end of cash flow statement i.e. their opening balance are added with the net changes in cash balance to determine their ending balance.
Determination of cash from operating activities under direct method
Net cash flow operating activities can be ascertained either by using direct method or indirect method. Under direct method, cash from operating activities is determined by deducting all cash expenses from the revenue generated in cash. Under indirect method, cash from operating activities is calculated on the basis of net income, non-operating and non-cash items and changes in current assets and current liabilities. Both methods are equally applicable, however, Nepal accounting standard emphasis direct method. Accounting to be clause 03 and report cash flow from operating activities using the direct method.
Cash collection from customers
Cash collection from customers includes the amount of cash sales and cash received from customers or credit sales. The sales reported by income statement are the combination of cash and credit sales. The cash generated through cash sales cash collection from credited sales is determined with the help of changes in the customer's account of bad debt written balance sheet. The amount of cash received is also affected by the amount of bad debt written off, bad debt recovered and discount allowed to customers. Following points are important to note while calculating cash collection form customers.
• An increase in debtors/accounts receivable/bills receivable account represents increase in credit sales, which reduces cash collection.
• A decrease in debtors/account receivable/biils receivable account represents cash collection from customers.
• An increase in provision for doubtful debt and provision for discount on debtors increase cash inflow and decrease in these accounts represent cash outflow.
• Bad debt recovered is a source of cash and discount allowed to customers is an application of cash.
Cash paid to suppliers
The major area of cash outflow under operating activities is the purchases of merchandise or goods purchase for the purpose of selling or manufacturing finished goods. Merchandise can be purchase either on cash or on credit. Sundry creditors, bill payable, accounts payable, suppliers account etc. are the account which show the condition of credit purchase during a particular period of time. The purchase or cost of goods sold shown by income statement represent both cash and credit purchase and cash paid to suppliers is determined with the help of cost of goods sold and changes is suppliers account and the position of inventory of merchandisers. Following points are importance to note while calculating cash paid to suppliers for the purchases of merchandise:
• An increase in creditors/accounts payable/bills payable account represents the credit purchase which decreases the cash outflow.
• An increase in ivestory represents purchase and decrease in inventory represents sales of merchandise.
• A decrease in creditors/account payable/bills payable account represent cash paid to suppliers which increase the cash outflow.
• Discount received from suppliers reduces the cash outflow
Cash paid to employees and for other expenses
Wages, salaries, rent general office expenses, selling and distribution expenses, depreciation are the example of operating expenses. Out of these expenses, depreciation is non-cash expenses. Income statement includes different types of operating and non-operating expenses, but only cash operating expenses are taken into account while determining cash paid to employees and for other expenses. Different types of operating and non-operating expenses expense losses as follows:
Interest payment
Interest on different types of loan is included either under operating activities or under financing activities. In the absence of any information, interest paid is considered as operating expenses and should be included under the operating section of cash flow statement. However the provision regarding the treatment of interest paid under Nepal accounting standard (NAS 03 sec 31, 32, 33 and 34) are as below:
• Cash flow from interest and dividend should be disclosed separately. Each should be classified in a consistent manner from period to period, operating, investing or financing activities.
• The total amount of interest paid during a period is disclosed in the cash flow statement whether it has been recognized as an expense in the income statement or capitalized.
• Interest paid is usually classified as operating cash flow flow a financing institution. However, there is no consensus on the classification for other enterprises. Interest paid may include under financing activities because interest paid is a cost of financing.
Tax payment
Tax paid is treated as cash outflow operating revenue. The amount of tax paid is determined on the basis of tax expense of the current year and position of outstanding tax. The method of ascertaining tax paid is as below:
Interest and dividend received
The provision regarding the treatment of interest and dividend received has been explained in section 31, 32, 33 and 34 under Nepal accounting standard (NAS-03). Cash flow from interest and dividend received should be disclosed separately. Each should be classified in a consistent manner from period to period, operating, investing or financing activities. Interest and dividend received are usually classified as operating cash inflow because they enter into the determination of net income or loss. Interest and dividend received may include under investing activities because they are treated as return on investment or shares, debentures and other assets. Interest and dividend is computed as below:
Cash from extra ordinary items
Cash sales and cash collection from customers, cash purchase and cash paid to suppliers, cash paid to employees and for other expenses, interest and dividend received or paid and tax paid are the normal or ordinary items relating with the operating activities. Beside these ordinary items, they are some other items concerned received with the operational cash flow of a business such as short term borrowing, compensation received from insurance companies etc. increase in the balance of extra ordinary items is treated as source or cash inflow and decrease in their balance is considered as cash outflow.
Cash and cash equivalent assets
All current assets and current liabilities are included under operating activities except cash and cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include cash in hand, cash at bank and any cash invested in short-term and highly liquid financing instruments. Generally, marketable securities cash as treasury bulls, commercial paper, and money market funds are also the examples of cash equivalents. If there are more than one item of cash and cash equivalents in the balance sheet, their opening and closing balance is computed as below:
Determination of cash from operating activities under indirect method
Under indirect method, cash flow from operating activities is determined on the basis of the following information:
• Net income or loss
• Non-cash expenses and losses, non-operating expenses, losses and amortizations
• Non-operating incomes and gain
• Changes in current assets (except cash & equivalents)
• Changes in current liabilities
Cash flow from investing activities
Cash flow from investing activities is the second part of cash flow statements. Investing activities are related with the purchases and sales of non-current assets such as plant and machinery, land and building, furniture and fixture etc. investing activities also include lending money and the purchase or sales of investment in securities activities explain the changes in cash position between to balance sheet dates due to the buying or selling of non-current assets. The cash inflows and outflows related with investing activities can be presented as below:
Cash flow from financing activities
The financing activates section of the cash flow statement shows the sources of fund generated through owner's capital and borrowed capital. Financing activities also include the repayment of debt and payment of cash dividend to shareholders. The major financing activities of a firm and impact of these activities on cash flow stream are presented as below:
Preparation of cash flow statement
Cash flow statement is prepared by combining the cash flows from operating activities investing activities and financing and financing activities. The main steps involved in the preparation of cash flow statement are presented in the following:
Cash flow statement under direct method
Combining the cash flows generated from operating, investing and financing activities, cash flow statement is prepared to show the net change on cash balance during a particular period. It can be prepared according to the direct direct or indirect method; the specimen of cash flow statement under direct method is as below:
Cash flow statement under indirect method
Cash flow statement can be prepared by using indirect method also. The difference between direct method and indirect method is only cash flows from operating activities. Cash flow from investing and financing activities are similar under direct and indirect methods. The format of cash flow statement under indirect method is as below:
Read More.....








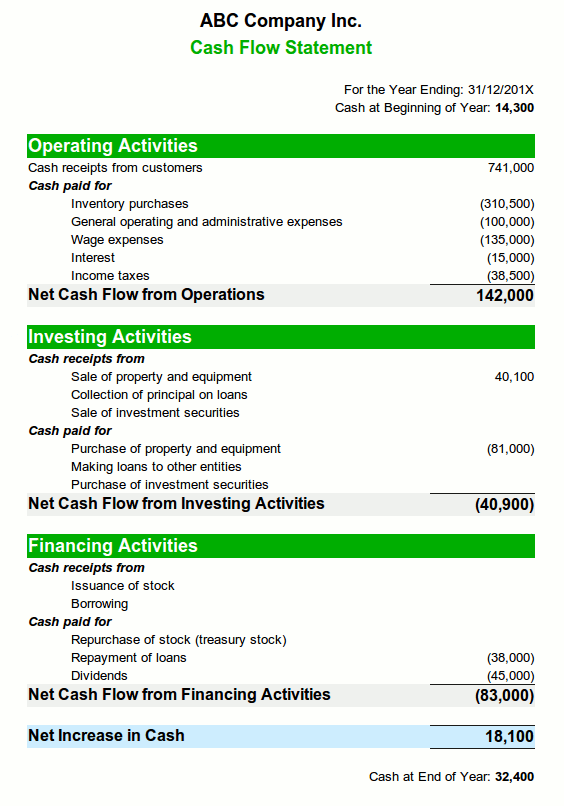
Primary objective of cash flow statement is to help management in taking decision and making plan by providing present information of cash inflow and outflow of any accounting period.
ReplyDeleteI think you should explore the articles on your website, You should also cover different different categories for articles as you writes awesome. Thanks for sharing this great article with us.
ReplyDeleteDaily cash flow statement
A cash flow statement provides information about the changes in cash and cash equivalents of a business by classifying cash flows into operating, investing and financing activities. It is a key report to be prepared for each accounting period for which financial statements are presented by an enterprise.
ReplyDeleteObjectives of preparing Cash Flow Statement:
- Cash flow statement shows inflow and outflow of cash and cash equivalents from various activities of a company during a specific period under the main heads i.e., operating activities, investing activities and financing activities.
- Information through the Cash Flow statement is useful in assessing the ability of any enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents and the needs of the enterprise to utilize those cash flows.
- Taking economic decisions requires an evaluation of the ability of an enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents, which is provided by the cash flow statement
Source: Leading Los Angeles Accounting Firms
A cash flow statement provides information about the changes in cash and cash equivalents of a business by classifying cash flows into operating, investing and financing activities. It is a key report to be prepared for each accounting period for which financial statements are presented by an enterprise.
ReplyDeleteObjectives of preparing Cash Flow Statement:
- Cash flow statement shows inflow and outflow of cash and cash equivalents from various activities of a company during a specific period under the main heads i.e., operating activities, investing activities and financing activities.
- Information through the Cash Flow statement is useful in assessing the ability of any enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents and the needs of the enterprise to utilize those cash flows.
- Taking economic decisions requires an evaluation of the ability of an enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents, which is provided by the cash flow statement
Source: Leading Los Angeles Accounting Firms
Cash flow shows the income and expenditure of a business.Thanks for sharing your blog.
ReplyDeletefinance guest post
Thank you for this information. I agree with you, As a business owner, it is important to know our Cash Flow
ReplyDeleteevery now and then. To track our expenses.
A cash flow statement is a financial statement that provides information about the cash inflows and outflows of a business during a specific period. It tracks the movement of cash into and out of the company and helps assess its liquidity, operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. The cash flow statement is an important tool for understanding the sources and uses of cash and evaluating a company's financial performance. Cash flow forecasting software
ReplyDelete