What is Activity based costing(ABC)?
What is Activity based costing(ABC)? & Traditional costing
Traditional costing
Concept of traditional costing
A number of activities are involved in manufacturing products of providing services. Some of such activities are purchase of materials, production planning, processing of orders, techn
ological assistance, quality control, accounting etc. if the per unit cost of product or service is calculated without considering the above activities in allocation and absorption of overhead, it is called the traditional costing method. In other words, if per unit cost is calculated on the basis of allocation and absorption of overhead on production units or direct labors hour or machine hour basis only, it is called the traditional method. This method is also termed as absorption costing or conventional costing. More specifically, under the traditional method, the overheads are not absorbed according to the activities rather it is done according to production units or labor hours or machine hours. It gives due emphasis to the production units not activities.
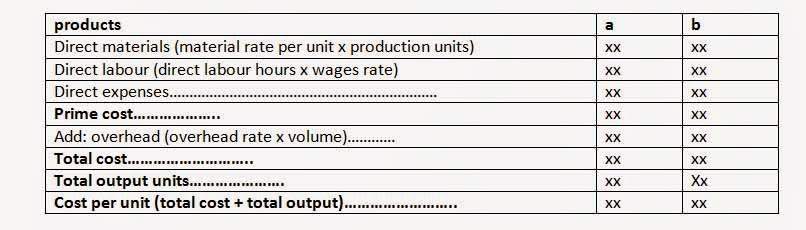
Cost statement under traditional costing
The way of calculating the cost per unit by preparing a cost statement is as under.
a. In the first stage, the total overhead should be ascertained.
b. In the second stage, the base of allocating the overhead s should be calculated. The bases many be production units or labor hours or machine hours.
c. In the third stage, the per unit or per hour overhead cost is calculated as under.
Overhead rate= total overhead/ total output or labour hour or machine hour
d. In the fifth stage, the overhead cost of each product or department is calculated multiplying the unit or hours by the respective rates, if per unit overhead cost is be calculated, divide the total overhead of each product or department by the respective units or hours.
e. In the sixth stage, the total cost is calculated by adding the overhead with the prime cost. Remember prime cost is comprised with direct material, direct labour and direct expenses.
f. At last, the per unit cost is calculated dividing the total cost by the units of the respective product or department.
Statement of cost traditional costing
Limitations of traditional costing
The following are the limitation of traditional costing systems.
• In traditional costing systems, overhead are absorbed on the basis of volume based activity in production unit or machine hour or labour hour. But there are some overhead, which are not dependant on them. So, it may not ascertain the accurate figure of cost.
• The traditional basis of segregating costs into fixed and variable elements on the basis of their behaviors is generally considered to be unrealistic. It is due to the with the growth of business, the costs have become more complex and complicated.
• The traditional method applied for absorbing overheads lays emphasis on the calculation and application of overhead recovery rates, which are accepted for the valuation of stock for the purposes of routing financial reporting. The management does not find these traditional methods helpful in making complicated decisions related to product strategies.
• The traditional absorption costing does not render any valuable assistance to multi-product concerns in making decisions regarding process technology, product-mix, product pricing etc.
Activity based costing is a systems of costing in which the overheads are assigned or related to activities or grouped into cost pools before they are assigned or related to cost objective i.e. products or services. It is a method of cost attribution to cost units on basis of benefits received from indirect activities. Activities become the focal points for cost accumulation. According to this systems total overhead are firstly traced into two or more production activities and then suitable cost drives are used to calculated per units cost of overheads. Product goods or rendering services. Activities based costing is made on the basis of cost driver requires for producing goods or rendering services. An activity is the cost center where the overhead are allocated whereas cost drive is the basis or indicator, which helps to trace overheads into product. This costing system assumes that activities are responsible for the incurred of cost and products create the demands for activities. Costs are charged to products based on individual product's use of each activity. An activity is an event is an event, task or unit of work with a specified purpose e.g., designing products. Setting up machines, operating machines and distributing products.
Limitations of traditional costing
The following are the limitation of traditional costing systems.
• In traditional costing systems, overhead are absorbed on the basis of volume based activity in production unit or machine hour or labour hour. But there are some overhead, which are not dependant on them. So, it may not ascertain the accurate figure of cost.
• The traditional basis of segregating costs into fixed and variable elements on the basis of their behaviors is generally considered to be unrealistic. It is due to the with the growth of business, the costs have become more complex and complicated.
• The traditional method applied for absorbing overheads lays emphasis on the calculation and application of overhead recovery rates, which are accepted for the valuation of stock for the purposes of routing financial reporting. The management does not find these traditional methods helpful in making complicated decisions related to product strategies.
• The traditional absorption costing does not render any valuable assistance to multi-product concerns in making decisions regarding process technology, product-mix, product pricing etc.
Activity based costing
Concept of activity based costingActivity based costing is a systems of costing in which the overheads are assigned or related to activities or grouped into cost pools before they are assigned or related to cost objective i.e. products or services. It is a method of cost attribution to cost units on basis of benefits received from indirect activities. Activities become the focal points for cost accumulation. According to this systems total overhead are firstly traced into two or more production activities and then suitable cost drives are used to calculated per units cost of overheads. Product goods or rendering services. Activities based costing is made on the basis of cost driver requires for producing goods or rendering services. An activity is the cost center where the overhead are allocated whereas cost drive is the basis or indicator, which helps to trace overheads into product. This costing system assumes that activities are responsible for the incurred of cost and products create the demands for activities. Costs are charged to products based on individual product's use of each activity. An activity is an event is an event, task or unit of work with a specified purpose e.g., designing products. Setting up machines, operating machines and distributing products.
R. Cooper and R.S. Kaplan defines "ABC systems calculated the costs of individual activities and assign costs to cost objects such as products and services on the basis of the activities undertaken to produce each product or services."
Likewise, according to T. Lucey, "activity based costing can be thought of as a method of charging overheads of cost units on the basis of benefits received from the particular indirect activities e.g. ordering planning, setting and so on, activities based costing seeks not only to allocate overhead to product cost on a more realistic basis than simple products volume, but also attempts to show the relationship between overhead costs and the activities than cause them."
From the above statements the following facts regarding activities based costing are summarized.
a. Production required activities.
b. Production work needs direct cost as well as indirect costs (overhead).
c. Direct cost and overhead cost are related with different activities.
d. Overhead cost is charged by showing the relationship between overhead and activities that causes them.
e. The overhead allocation on the basis of activities gives correct, accurate and realistic allocation to products. Thus, it gives the true picture of cost.
Significant terms in activities based costing
The activities based costing systems involves the use of the following terms:
a. Cost objects: generally, the products are cost objects, but the customers, services or locations to also be the cost objects.
b. Activities: these consist of the aggregate of different tasks and are concerned with functions associated with cost objectives. There are two types of activities:
i. Support activities
ii. Production process activities
Supports activities are, for example, schedule production, set up machine, purchase materials, and inspect items, customer orders, and supplier records etc. under the production process activity, machine production and assembled products are included within this production process.
Activities cost centers are, sometimes, similar to cost centers used under traditional costing systems in case the purchasing department and purchasing activity both are treated as cost centers, the support activity cost center also becomes identical to cost center taken under traditional costing system.
c. Cost pool: it is another name given to a cost center and therefore, an activity cost center may also be termed as an activity cost pool.
d. Cost drivers: the cases for incurrence of overhead cost are known as cost driver is factor the change of which results in a consequence charge in the total cost of a related object. It is any factor of force that causes a change in the cost of an activity. Cost drive may be divided into two parts:
i. Resource cost driver
ii. Activity cost driver
A resources cost driver is a measure of the quantity of resources consumed by an activity, it is used to assign the cost of a resource to an activity or cost pool. An activity cost driver is a measure of the frequency and interest of demand, place on activities by cost objects. It is used to assign activities cost to cost objects.
Classification of activities
As started earlier, activities are identified and classified into different categories or segments of their production process. The groping of activities is preferably done the different levels at which activities, are performed. Broadly, activities are classified into one of four activity categories:
a. Unit related activities: these are the activities which are performed each time of a unit is produced. They are repetitive. For example, direct labour hours, machine hours, power are used each time of a unit is produced. Direct materials and direct labour activities are laso unit related activities, although they are not overhead costs. Costs of unit related activities vary with the number of units produced.
b. Batch related activities: these are the activities, which are performed each time a batch of goods or products is produced. The costs of batch related activities vary with the number of batches but are fixed with respect to the number of units in each batch. Machine set ups, inspections, production scheduling, materials handling are example of batch related activities which are related to batches but not to individual products.
c. Product related activities: these are the activities, which are performed to support the production of each different type of product. Maintenance of equipment, engineering charges, testing routines, maintaining bills of materials, handling materials are some example of batch related activities.
d. Facility related activities: these are the activities, which are needed to sustain a factory's general manufacturing process. These activities are common to a variety of products and are most difficult to link to product specific activities. Examples of facility related activities are factory management, maintenance, security, plant depreciation. In ABC system, facility related activities caffeine costs are traded as period cost are they are found difficult to assign to different products. The costs associated which the first three categories-unit 1 related, batch related, product related are assigned to products, using cost drives that reflect the causes and effect relationship between activity, consumption and cost.
a. identifies the different activities: first the major activities are to be identified and then classified into different categories that have relationship with the different parts of the production process. Such identification is important because products required and activities consume costs, examples of some such activities are direct labour related activities, machine related activities and various supports activities, such as ordering, receiving, materials handling, production scheduling set up, packing and dispatching etc.
B. Determine the cost drivers of each activity: activity based costing is based on the assumption that cost behaviors are influenced by cost drivers. Therefore, in order to trace overhead costs to products, appropriate cost drives should be identified. In tradition product costing, the numbers of cost drivers used are few such as direct labour hours, machine hours, direct labour cost, units but ABC may use a multitude of cost drivers that relate costs more closely to the resource consumed and activities occurring. The factors that influence the cost of a particular activity are known as cost drivers. It should be understand that direct costs do not need cost drivers as they can be traced directly to a product. Direct costs are themselves cost drivers. However, all other indirect factory or manufacturing costs need cost driver. Cost drivers signify factors, farces or events that determine the costs of activities. Costs drovers are the links and they can link a pool of costs in an activities center to the product. Some of the activities and their cost drivers are mentioned below:
Likewise, according to T. Lucey, "activity based costing can be thought of as a method of charging overheads of cost units on the basis of benefits received from the particular indirect activities e.g. ordering planning, setting and so on, activities based costing seeks not only to allocate overhead to product cost on a more realistic basis than simple products volume, but also attempts to show the relationship between overhead costs and the activities than cause them."
From the above statements the following facts regarding activities based costing are summarized.
a. Production required activities.
b. Production work needs direct cost as well as indirect costs (overhead).
c. Direct cost and overhead cost are related with different activities.
d. Overhead cost is charged by showing the relationship between overhead and activities that causes them.
e. The overhead allocation on the basis of activities gives correct, accurate and realistic allocation to products. Thus, it gives the true picture of cost.
Significant terms in activities based costing
The activities based costing systems involves the use of the following terms:
a. Cost objects: generally, the products are cost objects, but the customers, services or locations to also be the cost objects.
b. Activities: these consist of the aggregate of different tasks and are concerned with functions associated with cost objectives. There are two types of activities:
i. Support activities
ii. Production process activities
Supports activities are, for example, schedule production, set up machine, purchase materials, and inspect items, customer orders, and supplier records etc. under the production process activity, machine production and assembled products are included within this production process.
Activities cost centers are, sometimes, similar to cost centers used under traditional costing systems in case the purchasing department and purchasing activity both are treated as cost centers, the support activity cost center also becomes identical to cost center taken under traditional costing system.
c. Cost pool: it is another name given to a cost center and therefore, an activity cost center may also be termed as an activity cost pool.
d. Cost drivers: the cases for incurrence of overhead cost are known as cost driver is factor the change of which results in a consequence charge in the total cost of a related object. It is any factor of force that causes a change in the cost of an activity. Cost drive may be divided into two parts:
i. Resource cost driver
ii. Activity cost driver
A resources cost driver is a measure of the quantity of resources consumed by an activity, it is used to assign the cost of a resource to an activity or cost pool. An activity cost driver is a measure of the frequency and interest of demand, place on activities by cost objects. It is used to assign activities cost to cost objects.
Classification of activities
As started earlier, activities are identified and classified into different categories or segments of their production process. The groping of activities is preferably done the different levels at which activities, are performed. Broadly, activities are classified into one of four activity categories:
a. Unit related activities: these are the activities which are performed each time of a unit is produced. They are repetitive. For example, direct labour hours, machine hours, power are used each time of a unit is produced. Direct materials and direct labour activities are laso unit related activities, although they are not overhead costs. Costs of unit related activities vary with the number of units produced.
b. Batch related activities: these are the activities, which are performed each time a batch of goods or products is produced. The costs of batch related activities vary with the number of batches but are fixed with respect to the number of units in each batch. Machine set ups, inspections, production scheduling, materials handling are example of batch related activities which are related to batches but not to individual products.
c. Product related activities: these are the activities, which are performed to support the production of each different type of product. Maintenance of equipment, engineering charges, testing routines, maintaining bills of materials, handling materials are some example of batch related activities.
d. Facility related activities: these are the activities, which are needed to sustain a factory's general manufacturing process. These activities are common to a variety of products and are most difficult to link to product specific activities. Examples of facility related activities are factory management, maintenance, security, plant depreciation. In ABC system, facility related activities caffeine costs are traded as period cost are they are found difficult to assign to different products. The costs associated which the first three categories-unit 1 related, batch related, product related are assigned to products, using cost drives that reflect the causes and effect relationship between activity, consumption and cost.
Procedures of activities based costing
The procedures of activities based costing are as under:a. identifies the different activities: first the major activities are to be identified and then classified into different categories that have relationship with the different parts of the production process. Such identification is important because products required and activities consume costs, examples of some such activities are direct labour related activities, machine related activities and various supports activities, such as ordering, receiving, materials handling, production scheduling set up, packing and dispatching etc.
B. Determine the cost drivers of each activity: activity based costing is based on the assumption that cost behaviors are influenced by cost drivers. Therefore, in order to trace overhead costs to products, appropriate cost drives should be identified. In tradition product costing, the numbers of cost drivers used are few such as direct labour hours, machine hours, direct labour cost, units but ABC may use a multitude of cost drivers that relate costs more closely to the resource consumed and activities occurring. The factors that influence the cost of a particular activity are known as cost drivers. It should be understand that direct costs do not need cost drivers as they can be traced directly to a product. Direct costs are themselves cost drivers. However, all other indirect factory or manufacturing costs need cost driver. Cost drivers signify factors, farces or events that determine the costs of activities. Costs drovers are the links and they can link a pool of costs in an activities center to the product. Some of the activities and their cost drivers are mentioned below:
d. Create a cost pool or cost center for each activity: in this step, factory overhead costs of the activity are determined and classified into homogeneous cost pools. A homogeneous cost pool is a collection of overhead costs that are logically related to the tasks being performed. A cost pool should be created for each activity. Cost pool is like center or activity center around which costs are accumulated. The importance assumption about activity center cost pools are that the costs in each cost pools are driven by homogeneous activities and strictly proportional to the activity.
e. Calculate the cost drive rates: after cost pool is defined and cost drivers are identified, the cost per unit of the cost driver is computed for that pool. This is called the pool rate or cost driver rate. The activity cost driver rates for each activity are calculated in the way in which overhead absorption rates would be calculated under the traditional absorption costing system. These activity cost driver rates are to be used for ascertaining the amount of overhead chargeable to various cost objects or products. These pool rates create links between costs and cost drivers used. This pool rate can be based on either planned or actual activity levels. It can be presented as follows:
f. Trace the cost of activities to products: in this step, the costs of each overhead pool are traced to products or cost objective which are the users of the resources. These, at the final stage, the cost pool, cost drive and the pool are combined to determine how much cost should be assigned to each by multiplying the activity cost drive rates by different amounts of each activity that each product or cost object consumes.
e. Calculate the cost drive rates: after cost pool is defined and cost drivers are identified, the cost per unit of the cost driver is computed for that pool. This is called the pool rate or cost driver rate. The activity cost driver rates for each activity are calculated in the way in which overhead absorption rates would be calculated under the traditional absorption costing system. These activity cost driver rates are to be used for ascertaining the amount of overhead chargeable to various cost objects or products. These pool rates create links between costs and cost drivers used. This pool rate can be based on either planned or actual activity levels. It can be presented as follows:
f. Trace the cost of activities to products: in this step, the costs of each overhead pool are traced to products or cost objective which are the users of the resources. These, at the final stage, the cost pool, cost drive and the pool are combined to determine how much cost should be assigned to each by multiplying the activity cost drive rates by different amounts of each activity that each product or cost object consumes.
Total overhead per product= total drivers for the product x cost driver rate
g. Computing the total costs of products or cost objects: finally, the total costs of the products or cost objects shall be computed by adding all direct and indirect costs assigned to them.
Comparison between traditional costing and activity based costing
Following are the main different between activity based costing and traditional costing system:
a. Under ACB system, overhead costs are identified to each major activity instead of the departments as under traditional costing system. It results in greeter number of cost center under ABC system.
b. The term 'cost driver' is not used traditional costing systems. Populate terms are basis of allocation or apportionment. Under ABC systems, cost drivers are fewer in number for the purpose of changing overhead to products.
c. ABC system uses separate rates for supporting centers and these is no re-apportionment to production centers, as is the case under traditional costing systems.
Advantages of activity based costing
The following are the main advantages of ABC system:
a. It gives accurate and true figure of cost due to different overhead costs are distributed on the basis of different suitable cost drivers.
b. It helps understanding the behaviors of overhead costs and their relationship to products, services, customers and markets segments.
c. Since all the overhead are distributed on the basis of suitable cost drivers, so that, proper record keeping of different cost drivers are kept. So it assists to control over the costs.
d. Its helps the management in taking better decision relating to products strategies, product designs, product mix and marketing.
e. ABC systems are very helpful in making the evaluation of new process technology in multi-product concerns.
f. It provides the right information for performance measurement because if focuses on activities rather than resources.
g. This system makes available a systematic report on the resources spending as well as on resources consumption.
h. It provides accurate information on profit margin and performance measurement for profit improvement.
Limitations of activity based costing system
The following are the limitation of the ABC system:
a. It is complex in comparison of traditional costing, due to different cost drivers are used to distribute different overhead.
b. To identifying the suitable cost driver is tough job. If proper/right cost drivers is not chosen the overhead absorption may not gives true figure.
c. It is costly; because it needs specialized accounting systems and skilled accounting for that we have to pay more.
d. It is suitable for large organization only.
e. As ABC concept is still in primary stage of development, its applicability is still doubtful.
Impact of volume diversity
If the production of different products is done in similar quantities, there will not be a signification difference on per unit cost and profit between the traditional and activity based costing. On the other hand, when the quantities of the products being produced vary sigficantly, some abnormal differences may exist on the per unit cost as well as profit between these costing methods. Such an abnormal difference in per unit cost and profit that cause due to the different in volume is called the impact of volume diversity. The following example shows the impact of volume diversity.
c. Since all the overhead are distributed on the basis of suitable cost drivers, so that, proper record keeping of different cost drivers are kept. So it assists to control over the costs.
d. Its helps the management in taking better decision relating to products strategies, product designs, product mix and marketing.
e. ABC systems are very helpful in making the evaluation of new process technology in multi-product concerns.
f. It provides the right information for performance measurement because if focuses on activities rather than resources.
g. This system makes available a systematic report on the resources spending as well as on resources consumption.
h. It provides accurate information on profit margin and performance measurement for profit improvement.
Limitations of activity based costing system
The following are the limitation of the ABC system:
a. It is complex in comparison of traditional costing, due to different cost drivers are used to distribute different overhead.
b. To identifying the suitable cost driver is tough job. If proper/right cost drivers is not chosen the overhead absorption may not gives true figure.
c. It is costly; because it needs specialized accounting systems and skilled accounting for that we have to pay more.
d. It is suitable for large organization only.
e. As ABC concept is still in primary stage of development, its applicability is still doubtful.
Impact of volume diversity
If the production of different products is done in similar quantities, there will not be a signification difference on per unit cost and profit between the traditional and activity based costing. On the other hand, when the quantities of the products being produced vary sigficantly, some abnormal differences may exist on the per unit cost as well as profit between these costing methods. Such an abnormal difference in per unit cost and profit that cause due to the different in volume is called the impact of volume diversity. The following example shows the impact of volume diversity.
In the above example, there no different in the per unit cost as well as profit under traditional method irrespective of the volume different. The per unit cost is Rs20 and per unit profit is Rs 5 under both the products. Contrary to this, there are different in the per unit cost as well as profit under activity based costing. As a result, the cost per unit of product is high with product 'p1' resulting in loss where the per unit cost is low resulting in profit with the product 'p2'. Though the total profit remains the same, the p2 is more profitable than p1. In this way, activity based costing is helpful in assessing the profitable of each product.
Activity based profitability analysis
The method of calculating the profit under traditional and activity based costing are different. Under, traditional method the gross profit/ loss are calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from sales. The net profit/loss is calculated by subtracting the operating expenses from the gross profit. But, profit/loss is calculated with different level as unit level, production level, product line level and plant level.
According to these different levels, the income statatement under activity based costing is prepared as under.
1. State the limitation of traditional costing system.
The following are the limitations of traditional system.
a. In traditional costing system, overhead are absorbed on the basis of volume based activity in production unit or machine hour or labour hour. But t here is some overhead, which are not dependant on them. So, it may not ascertain the accurate figure of cost.
b. The traditional basis of segregating costs into fixed and variable elements on the basis of their behavior is generally considered to be unrealistic. It is due to the fact that with the growth of business, the costs have become more complex and complicated.
c. The traditional method applied for absorbing overhead lays emphasis on the calculation and application of overhead recovery rates, which are acceptable for the valuation of stocks for the purpose of routine financial methods helpful in making complicated decisions unrelated to product strategies.
d. The traditional absorption costing does not render any valuable assistance to multi-product concerns in making decisions regarding process technology, product-mix, product pricing etc.
2. What do you mean by Activity Based Costing (ABC)?
Activity based costing is a system of costing in which the overhead are assigned or related to activities or grouped into cost pool before they are assigned or related to cost objects i.e. products or serves. It is a method of cost attribution to cost units on the basis of benefits received form indirect activities'.
Activities become the focal points for cost accumulation according to this system total overhead are firstly traced into two or more production activities and then suitable cost drivers are used to calculated per unit cost of overheads. Product cost determination under activity based costing in made on the basis of cost drivers required for producing goods or rendering services whereas cost drive is the basis or indirect, which helps to trace overhead into product.
3. Mention the advantages of Activity based costing.
The following are the main advantages of ABC system:
a. It gives accurate and true figure of cost due to different overhead costs are distributed on the basis of different suitable cost drives.
b. It helps understanding the behavior of overhead costs and their relationship to products, services, customer and markets segments.
c. Since all the overhead are distributed on the basis of suitable cost drivers, so that, proper record keeping of different cost drivers are kept. So it assists to control over the costs.
d. It helps the management in taking better decision relating to product strategies, product designs, product mix and making.
e. ABC system is very helpful in making the evaluation of new process technologies in multi-product concerns.
Formula of list
1. Cost statement under traditional costing
Overhead rate= total overhead / total output or labour hour or machine hour
2. Total overhead per product = total drivers for the product x cost driver rate
3. Cost driver rate = overheads/ nos. where nos. = total number of cost drivers







No comments:
Post a Comment